Dari desktop publishing and typesetting services
Our Dari DTP and typesetting services include:
- Dari Document Translations
- Dari Proofreading
- Dari Desktop publishing and typesetting using all major publishing software
- Desktop publishing into over 120 languages
- Quality assurance checking throughout the process
- Localisation of graphics in documents
- Dedicated project manager
- Fast turnaround
- Print ready PDFs set to your specifications
- 100% work carried out In-house by our own DTP studio
Clients:
We work for companies and organisations such as Disney, Vidal Sassoon, and Jaguar Land Rover, to list a few. Plus international aid agencies such as Amnesty International, Refugee Action, UNICEF and the Refugee Council as well as many translation agencies and publishing companies all over the world.
A simple guide to localising InDesign files using translation software
By using an IDML file exported from InDesign we can speed up the translation and DTP process when using translation memory software. This method keeps all the formatting from the original InDesign file such as links, character and paragraph styles and fonts plus any interactive elements such as cross-references.
What is the difference between desktop publishing and typesetting
- Typesetting is also defined as: Typesetting is the process, the craft, of setting the type for a document, not to be confused with typography, which is the art of designing the type.
- Desktop publishing is also defined as The production of printed matter by means of a printer linked to a desktop computer, with special software.
Desktop publishing tips for localising English materials
- In some designs the pages are simply filled with text, leaving no room for text expansion. Most languages (with some notable exceptions) run longer than English and some of them run much longer. This causes the localised versions to have to make some sort of compromise: either text becomes smaller or a condensed font is used, or some material is completely cut out for brevity. Neither scenario is ideal, so it is much better to consider this aspect of the task at the design stage.
- Overuse of text formatting features such as drop caps, CAPITALISED TEXT, coloured text, bold text and italic text etc. can slow down the localisation process, as the formatting needs to be applied to the precise word or phrase in translation that is equivalent to the English. Sometimes, this does not work at all if the target language has a dramatically different word order.
- Embedded, non-editable text in images require extra attention and can slow things down dramatically, especially when over the main part of the image. Where possible, the text should be made available for editing in InDesign. If not, we will require all of the PSD files to work with.
- Avoid designing paragraphs or “word clouds” with mixed font sizes that look good in English but have no chance of being replicated in the target language: quite often they do not have the same impact when localised and can often be “lost in translation”. Furthermore, due to word order difference, keywords in English at the beginning of a sentence might end up in the middle or at the end of the sentence when translated.
- One of the most frequent issues we encounter is the incorrect and inconsistent usage of style sheets, in particular where one style has been used but in some instances, bold text, italics or even different fonts have been changed manually. This can cause significant delays in the localisation process.
- Sending the artwork to be typeset BEFORE it is signed off by the client is never a good idea, and neither are new design changes after we have already started the work. We can do nothing in situations like these where significant changes are requested mid-project but start again and present new figures for the work, delaying work and incurring further costs for the client.
Khmer desktop publishing and typesetting services
Our Khmer DTP and typesetting services include:
- Khmer Document Translations
- Khmer Proofreading
- Khmer Desktop publishing and typesetting using all major publishing software
- Desktop publishing into over 100 languages
- Quality assurance checking throughout the process
- Localisation of graphics in documents
- Dedicated project manager
- Fast turnaround
- Print ready PDFs set to your specifications
- 100% work carried out In-house by our own DTP studio
Clients:
We work for companies and organisations such as Disney, Vidal Sassoon, and Jaguar Land Rover, to list a few. Plus international aid agencies such as Amnesty International, Refugee Action, UNICEF and the Refugee Council as well as many translation agencies and publishing companies all over the world.
A simple guide to localising InDesign files using translation software
By using an IDML file exported from InDesign we can speed up the translation and DTP process when using translation memory software. This method keeps all the formatting from the original InDesign file such as links, character and paragraph styles and fonts plus any interactive elements such as cross-references.
Click here to read more information
What is the difference between desktop publishing and typesetting
- Typesetting is also defined as: Typesetting is the process, the craft, of setting the type for a document, not to be confused with typography, which is the art of designing the type.
- Desktop publishing is also defined as The production of printed matter by means of a printer linked to a desktop computer, with special software.
Desktop publishing tips for localising English materials
- In some designs the pages are simply filled with text, leaving no room for text expansion. Most languages (with some notable exceptions) run longer than English and some of them run much longer. This causes the localised versions to have to make some sort of compromise: either text becomes smaller or a condensed font is used, or some material is completely cut out for brevity. Neither scenario is ideal, so it is much better to consider this aspect of the task at the design stage.
- Overuse of text formatting features such as drop caps, CAPITALISED TEXT, coloured text, bold text and italic text etc. can slow down the localisation process, as the formatting needs to be applied to the precise word or phrase in translation that is equivalent to the English. Sometimes, this does not work at all if the target language has a dramatically different word order.
- Embedded, non-editable text in images require extra attention and can slow things down dramatically, especially when over the main part of the image. Where possible, the text should be made available for editing in InDesign. If not, we will require all of the PSD files to work with.
- Avoid designing paragraphs or “word clouds” with mixed font sizes that look good in English but have no chance of being replicated in the target language: quite often they do not have the same impact when localised and can often be “lost in translation”. Furthermore, due to word order difference, keywords in English at the beginning of a sentence might end up in the middle or at the end of the sentence when translated.
- One of the most frequent issues we encounter is the incorrect and inconsistent usage of style sheets, in particular where one style has been used but in some instances, bold text, italics or even different fonts have been changed manually. This can cause significant delays in the localisation process.
- Sending the artwork to be typeset BEFORE it is signed off by the client is never a good idea, and neither are new design changes after we have already started the work. We can do nothing in situations like these where significant changes are requested mid-project but start again and present new figures for the work, delaying work and incurring further costs for the client.
Myanmar desktop publishing and typesetting services
Our Myanmar DTP and typesetting services include:
- Myanmar Document Translations
- Myanmar Proofreading
- Myanmar Desktop publishing and typesetting using all major publishing software
- Desktop publishing into over 100 languages
- Quality assurance checking throughout the process
- Localisation of graphics in documents
- Dedicated project manager
- Fast turnaround
- Print-ready PDFs set to your specifications
- 100% work carried out in-house by our own DTP studio
We work for companies and organisations such as Disney, Vidal Sassoon, and Jaguar Land Rover, to list a few. Plus international aid agencies such as Amnesty International, Refugee Action, UNICEF and the Refugee Council as well as many translation agencies and publishing companies all over the world.
Why choose Adelphi
Clients often come to us with Myanmar translations produced by another agency or freelance linguist. However, in many cases, the translator will not have used a font that is compatible with any typesetting software, making the translation unusable. In cases where the wrong font is used, the entire translation has to be rewritten using a professional font, thus incurring additional costs for you.
Thanks to Adelphi’s typesetting expertise, we understand that Myanmar fonts are often incompatible with each other and cannot simply be swapped with other Myanmar fonts. When we produce the Myanmar translation, we make sure that it is translated using a professional font that works in typesetting software packages.
A simple guide to localising InDesign files using translation software
By using an IDML file exported from InDesign we can speed up the translation and DTP process when using translation memory software. This method keeps all the formatting from the original InDesign file such as links, character and paragraph styles and fonts plus any interactive elements such as cross-references.
Click here to read more information
What is the difference between desktop publishing and typesetting
- Typesetting is also defined as: Typesetting is the process, the craft, of setting the type for a document, not to be confused with typography, which is the art of designing the type.
- Desktop publishing is also defined as: The production of printed matter by means of a printer linked to a desktop computer, with special software.
Desktop publishing tips for localising English materials
- In some designs the pages are simply filled with text, leaving no room for text expansion. Most languages (with some notable exceptions) run longer than English and some of them run much longer. This causes the localised versions to have to make some sort of compromise: either text becomes smaller or a condensed font is used, or some material is completely cut out for brevity. Neither scenario is ideal, so it is much better to consider this aspect of the task at the design stage.
- Overuse of text formatting features such as drop caps, CAPITALISED TEXT, coloured text, bold text and italic text etc. can slow down the localisation process, as the formatting needs to be applied to the precise word or phrase in translation that is equivalent to the English. Sometimes, this does not work at all if the target language has a dramatically different word order.
- Embedded, non-editable text in images require extra attention and can slow things down dramatically, especially when over the main part of the image. Where possible, the text should be made available for editing in InDesign. If not, we will require all of the PSD files to work with.
- Avoid designing paragraphs or “word clouds” with mixed font sizes that look good in English but have no chance of being replicated in the target language: quite often they do not have the same impact when localised and can often be “lost in translation”. Furthermore, due to word order difference, keywords in English at the beginning of a sentence might end up in the middle or at the end of the sentence when translated.
- One of the most frequent issues we encounter is the incorrect and inconsistent usage of style sheets, in particular where one style has been used but in some instances, bold text, italics or even different fonts have been changed manually. This can cause significant delays in the localisation process.
- Sending the artwork to be typeset BEFORE it is signed off by the client is never a good idea, and neither are new design changes after we have already started the work. We can do nothing in situations like these where significant changes are requested mid-project but start again and present new figures for the work, delaying work and incurring further costs for the client.
Voice-overs for Best Western in 18 Languages
Danish, Dutch, English UK, Finnish, French, Japanese, German, Greek, Italian, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish, Turkish, Russian, Chinese, and Korean.
Adelphi are looking for a Subtitling and Voice-over engineer
Adelphi are looking for a Subtitling and voice-over engineer
Adelphi Studio based in Sheffield UK are looking for someone who has experience in producing of subtitles and voice-over recording.
Voice-overs
Reporting to the Studio Manager, you would be largely responsible for recording and post production of voice overs, as well as digital marketing in quieter periods. You will be expected to roll up your sleeves and get stuck into any task that needs doing! No day will be the same, but activities might include:
€¢ Undertaking training in all the software used by the organisation
€¢ Sourcing voice-artists in the languages required. These can be locals or professional artists around the world.
€¢ Holding auditions in our studio recording samples of their voices for clients and our website www.adelphistudio.com
€¢ Recording the work when the client has agreed the artist of their choice.
€¢ Post-production audio
€¢ Dealing with telephone and email enquiries
€¢ Maintaining social media streams such as Facebook, Vimeo and Twitter
€¢ Maintaining the company website and blog
Subtitling
Basic knowledge of SRT files. Knowledge of Final Cut Pro, Compressor, After Effects and Premiere Pro will be useful but not essential as training will be provided?
Send you C.V to nigel@adelphitranslations.com or simply fill in the form below:
Articulate Storyline Localisation into any language
Articulate Storyline Localisation
Adelphi can localise your Articulate Storyline course into any language. For Storyline localization, we use a fully supported and tested process, which consists of four stages:
Export the original text:
The English text from the course is exported into a table in Word or a translation memory file (XLIFF format). This includes buttons, sliders and captions that are not part of the main body of text.
Translate the exported text:
We contact a professional, experienced translators working into their native tongue and ask them to translate your content. The linguists will be selected based on their skill and understanding of the subject matter: we have a translator for every specialisation. All of our linguists have a minimum of three years’ commercial experience and are vetted based on quality and punctuality.
Import the translated text:
The translations then go to our production department, where the foreign-language content is imported back into the course, populating the text boxes, button, sliders and captions with the translated text.
Quality testing:
We perform quality checks on the result, making sure that the process was successful: that there are no errors in functionality and any text that is longer in the foreign language than the source fits comfortably in the template.
Subtitling, Voice-overs, Typesetting
Adelphi also offers subtitling, voice-over and typesetting services, meaning that if your course has any video or printed word elements, we can produce these in your target languages as well. We understand that rolling out a new course can be a complex undertaking, which is why our project managers are set up to handle everything about the localisation process for you in one place.
Azerbaijani desktop publishing and typesetting services
Our Azerbaijani DTP services include:
- Azerbaijani Document Translations
- Azerbaijani Proofreading
- Azerbaijani Desktop publishing using all major publishing software
- Desktop publishing in over 120 languages
- DTP QA quality assurance checking of documents
- Localisation of graphics in documents
- Dedicated project manager
- Fast turnaround
- Print ready PDFs set to your specifications
- 100% work carried out In-house by our own DTP studio
Clients
We work for companies and organisations such as Disney, Vidal Sassoon, and Jaguar Land Rover, to list a few. Plus international aid agencies such as Amnesty International, Refugee Action, UNICEF and the Refugee Council as well as many translation agencies and publishing companies all over the world.
A simple guide to localising InDesign files using translation software
By using an IDML file exported from InDesign we can speed up the translation and DTP process when using translation memory software. This method keeps all the formatting from the original InDesign file such as links, character and paragraph styles and fonts plus any interactive elements such as cross-references.
Click here to read more information
What is the difference between desktop publishing and typesetting?
- Typesetting is also defined as: Typesetting is the process, the craft, of setting the type for a document, not to be confused with typography, which is the art of designing the type.
- Desktop publishing is also defined as The production of printed matter by means of a printer linked to a desktop computer, with special software.
Desktop Publishing tips when designing English materials for translation
- In some designs the pages are simply filled with text, leaving no room for text expansion. Most languages (with some notable exceptions) run longer than English and some of them run much longer. This causes the localised versions to have to make some sort of compromise: either text becomes smaller or a condensed font is used, or some material is completely cut out for brevity. Neither scenario is ideal, so it is much better to consider this aspect of the task at the design stage.
- Overuse of text formatting features such as drop caps, CAPITALISED TEXT, coloured text, bold text and italic text etc. can slow down the localisation process, as the formatting needs to be applied to the precise word or phrase in translation that is equivalent to the English. Sometimes, this does not work at all if the target language has a dramatically different word order.
- Embedded, non-editable text in images require extra attention and can slow things down dramatically, especially when over the main part of the image. Where possible, the text should be made available for editing in InDesign. If not, we will require all of the PSD files to work with.
- Avoid designing paragraphs or “word clouds” with mixed font sizes that look good in English but have no chance of being replicated in the target language: quite often they do not have the same impact when localised and can often be “lost in translation”. Furthermore, due to word order difference, keywords in English at the beginning of a sentence might end up in the middle or at the end of the sentence when translated.
- One of the most frequent issues we encounter is the incorrect and inconsistent usage of style sheets, in particular where one style has been used but in some instances, bold text, italics or even different fonts have been changed manually. This can cause significant delays in the localisation process.
- Sending the artwork to be typeset BEFORE it is signed off by the client is never a good idea, and neither are new design changes after we have already started the work. We can do nothing in situations like these where significant changes are requested mid-project but start again and present new figures for the work, delaying work and incurring further costs for the client.
Yoruba desktop publishing and typesetting services
Our Yoruba DTP and typesetting services include:
- Yoruba Document Translations
- Yoruba Proofreading
- Yoruba Desktop publishing and typesetting using all major publishing software
- Desktop publishing into over 100 languages
- Quality assurance checking throughout the process
- Localisation of graphics in documents
- Dedicated project manager
- Fast turnaround
- Print ready PDFs set to your specifications
- 100% work carried out in-house by our own DTP studio
Clients:
We work for companies and organisations such as Disney, Vidal Sassoon, and Jaguar Land Rover, to list a few. Plus international aid agencies such as Amnesty International, Refugee Action, UNICEF and the Refugee Council as well as many translation agencies and publishing companies all over the world.
A simple guide to localising InDesign files using translation software
By using an IDML file exported from InDesign we can speed up the translation and DTP process when using translation memory software. This method keeps all the formatting from the original InDesign file such as links, character and paragraph styles and fonts plus any interactive elements such as cross-references.
Click here to read more information
What is the difference between desktop publishing and typesetting
- Typesetting is also defined as: Typesetting is the process, the craft, of setting the type for a document, not to be confused with typography, which is the art of designing the type.
- Desktop publishing is also defined as The production of printed matter by means of a printer linked to a desktop computer, with special software.
Desktop publishing tips for localising English materials
- In some designs the pages are simply filled with text, leaving no room for text expansion. Most languages (with some notable exceptions) run longer than English and some of them run much longer. This causes the localised versions to have to make some sort of compromise: either text becomes smaller or a condensed font is used, or some material is completely cut out for brevity. Neither scenario is ideal, so it is much better to consider this aspect of the task at the design stage.
- Overuse of text formatting features such as drop caps, CAPITALISED TEXT, coloured text, bold text and italic text etc. can slow down the localisation process, as the formatting needs to be applied to the precise word or phrase in translation that is equivalent to the English. Sometimes, this does not work at all if the target language has a dramatically different word order.
- Embedded, non-editable text in images require extra attention and can slow things down dramatically, especially when over the main part of the image. Where possible, the text should be made available for editing in InDesign. If not, we will require all of the PSD files to work with.
- Avoid designing paragraphs or “word clouds” with mixed font sizes that look good in English but have no chance of being replicated in the target language: quite often they do not have the same impact when localised and can often be “lost in translation”. Furthermore, due to word order difference, keywords in English at the beginning of a sentence might end up in the middle or at the end of the sentence when translated.
- One of the most frequent issues we encounter is the incorrect and inconsistent usage of style sheets, in particular where one style has been used but in some instances, bold text, italics or even different fonts have been changed manually. This can cause significant delays in the localisation process.
- Sending the artwork to be typeset BEFORE it is signed off by the client is never a good idea, and neither are new design changes after we have already started the work. We can do nothing in situations like these where significant changes are requested mid-project but start again and present new figures for the work, delaying work and incurring further costs for the client.
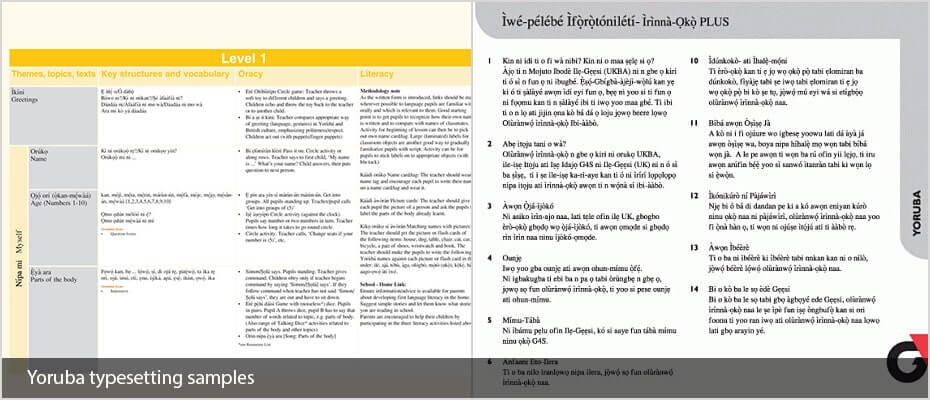
Yoruba Typesetting
Adelphi has its own in-house studio providing Yoruba Typesetting Services. Our entire Yoruba typesetting is handled in-house and carried out by our own experienced typesetters. We produce all kinds of printed materials in Yoruba including corporate brochures, packaging, business cards, posters and manuals.
Typesetting is also known as desktop publishing (DTP).
Adelphi Translations have been producing Yoruba typesetting over for over 15 years. We produce all kinds of Yoruba typesetting materials including corporate brochures, packaging, business cards, posters and manuals, not just in Yoruba but also in over 60 other languages. We work for companies and organisations such as Disney, Vidal Sassoon, and Jaguar Land Rover, to list a few. Plus international aid agencies such as Amnesty International, Refugee Action, UNICEF and the Refugee Council as well as many translation agencies all over the world.
We use all of the industry standard software packages including InDesign, QuarkXpress, FrameMaker, Illustrator and all Microsoft software.
Welsh desktop publishing and typesetting services
Our Welsh DTP and typesetting services include:
- Welsh Document Translations
- Welsh Proofreading
- Welsh Desktop publishing and typesetting using all major publishing software
- Desktop publishing into over 100 languages
- Quality assurance checking throughout the process
- Localisation of graphics in documents
- Dedicated project manager
- Fast turnaround
- Print ready PDFs set to your specifications
- 100% work carried out in-house by our own DTP studio
Clients:
We work for companies and organisations such as Disney, Vidal Sassoon, and Jaguar Land Rover, to list a few. Plus international aid agencies such as Amnesty International, Refugee Action, UNICEF and the Refugee Council as well as many translation agencies and publishing companies all over the world.
A simple guide to localising InDesign files using translation software
By using an IDML file exported from InDesign we can speed up the translation and DTP process when using translation memory software. This method keeps all the formatting from the original InDesign file such as links, character and paragraph styles and fonts plus any interactive elements such as cross-references.
Click here to read more information
What is the difference between desktop publishing and typesetting
- Typesetting is also defined as: Typesetting is the process, the craft, of setting the type for a document, not to be confused with typography, which is the art of designing the type.
- Desktop publishing is also defined as The production of printed matter by means of a printer linked to a desktop computer, with special software.
Desktop publishing tips for localising English materials
- In some designs the pages are simply filled with text, leaving no room for text expansion. Most languages (with some notable exceptions) run longer than English and some of them run much longer. This causes the localised versions to have to make some sort of compromise: either text becomes smaller or a condensed font is used, or some material is completely cut out for brevity. Neither scenario is ideal, so it is much better to consider this aspect of the task at the design stage.
- Overuse of text formatting features such as drop caps, CAPITALISED TEXT, coloured text, bold text and italic text etc. can slow down the localisation process, as the formatting needs to be applied to the precise word or phrase in translation that is equivalent to the English. Sometimes, this does not work at all if the target language has a dramatically different word order.
- Embedded, non-editable text in images require extra attention and can slow things down dramatically, especially when over the main part of the image. Where possible, the text should be made available for editing in InDesign. If not, we will require all of the PSD files to work with.
- Avoid designing paragraphs or “word clouds” with mixed font sizes that look good in English but have no chance of being replicated in the target language: quite often they do not have the same impact when localised and can often be “lost in translation”. Furthermore, due to word order difference, keywords in English at the beginning of a sentence might end up in the middle or at the end of the sentence when translated.
- One of the most frequent issues we encounter is the incorrect and inconsistent usage of style sheets, in particular where one style has been used but in some instances, bold text, italics or even different fonts have been changed manually. This can cause significant delays in the localisation process.
- Sending the artwork to be typeset BEFORE it is signed off by the client is never a good idea, and neither are new design changes after we have already started the work. We can do nothing in situations like these where significant changes are requested mid-project but start again and present new figures for the work, delaying work and incurring further costs for the client.
Adelphi Translations Limited is a company registered in England and Wales.
Company Number 06989736 · Registered Office Barnsley Digital Media Centre, County Way, Barnsley, S70 2JW, UK